
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane (D3)
| Chemical Name: | Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane |
| Product Category: | Silicone Intermediate – Product |
| Structural Formula: | 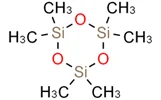  |
| CAS No.: | 541-05-9 |
| EINECS: | 208-765-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C6H18O3Si3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 222.46 |
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane Description
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane (D3) CAS 541-05-9, with the molecular formula C6H18O3Si3, is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 75°C and a shrinkage rate of 0.6-0.8%. It is primarily used for shrinkage treatment in silicone rubber.
Also known as cyclotrimethylsiloxane, hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane (D3) is a key silicone intermediate. It serves as a raw material for synthesizing silicone polymers and is widely used in the production of specialized silicone compounds, including surface treatment agents, coupling agents, and cross-linking agents.
| Melting point | 50-64 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 134 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.02 |
| Vapor Density | 1 (vs air) |
| Flash point | 95°F |
| Storage conditions | Flammables area |
| Water solubility | may decompose |
| Sensitivity | Moisture Sensitive Moisture Resistant Water Resistant |
| Stability | Stable, but moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Properties | white crystal, melting point 75°C, shrinkage rate 0.6-0.8%, used for silicone rubber shrinkage treatment |
| Uses | In addition to synthesizing general organosilicon polymers, it can also be used to prepare specific organosilicon compounds as various surface treatment agents, coupling agents, cross-linking agents, etc. |
| Hazardous |
|
| Transportation & Safety info |
|
| Packaging |
|
| Sample |
|
| Inventory items |
|
| Price |
|
Packaging Specifications




Jessica G.
Get the Latest Pricing and Information
- Quick and helpful reply within 8 hours;
- Tailored solutions provided for your project;
- One-stop purchasing service.
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane: Guide
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane (D3) CAS 541-05-9 is a key intermediate in the production of methyl vinyl silicone rubber and an essential raw material for synthesizing various polymer compounds.
In the presence of sodium silanolate, potassium silanolate, or concentrated sulfuric acid, D3 undergoes Si-O-Si bond cleavage and rearrangement, forming a mixture of linear polysiloxanes and cyclic siloxanes. This catalytic process exhibits equilibrium characteristics, where both ring-opening polymerization and chain degradation occur, leading to the formation of high-molecular-weight polymers.
When reacted with excess sodium hydroxide methanol solution, it produces sodium dimethylsilanediol. Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane can be obtained from the high-temperature cracking of hydrolyzed dimethyldichlorosilane (DMDCS) with KOH. It is commonly found in mixed cyclic siloxane formulations, widely used in the production of dimethicones and silicone rubbers.












