N-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane
| Chemical Name: | n-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane |
| Alias: | 1-(Trimethoxysilyl)dodecane |
| Product Category: | Alkylsilane – Silanes |
| Structural Formula: | 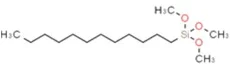 |
| CAS No.: | 3069-21-4 |
| EINECS: | 221-332-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H34O3Si |
| Molecular Weight: | 290.51 |
N-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane Description
N-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane (CAS 3069-21-4) is a colorless, transparent liquid, known for its excellent reactivity with minerals when exposed to moisture. This monomeric alkylalkoxysilane deeply penetrates substrates, forming a durable protective surface around each microscopic particle, significantly enhancing weather resistance. It dissolves easily in organic solvents to create clear, stable solutions.
Product Applications
- Improves water resistance and bonding between inorganic fillers (e.g., glass, silica, kaolin, mica, talc powder) and organic materials (e.g., plastic, rubber, adhesives), enhancing mechanical properties.
- Protects blank and coated glass (including optical anti-reflective coatings, vacuum AR coatings, and reflective coatings).
- Shields optical components and precise equipment with metal frames or graduations.
- Protects outdoor historical relics from corrosion, freeze damage, and efflorescence.
| Alias | 1-(Trimethoxysilyl)dodecane |
| Melting point | -40°C |
| Boiling point | 125 °C |
| density | 0.89 |
| refractive index | 1.4274 |
| Fp | 108°C |
| Specific Gravity | 0.89 |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 7: reacts slowly with moisture/water |
| BRN | 2356323 |
| Appearance | Colorless Clear Liquid |
| Purity | 96% Min |
| Hazardous |
|
| Transportation & Safety info |
|
| Packaging |
|
| Sample |
|
| Inventory items |
|
| Price |
|
Packaging Specifications


Jessica G.
Get in touch to Get
- Quick and helpful reply within 8 hours;
- Tailored solutions provided for your project;
- One-stop purchasing service.
N-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane: Guide
N-Dodecyltrimethoxysilane, an alkyltrialkoxysilane, is a trifunctional compound with all three alkoxy groups capable of hydrolysis. It is highly soluble in organic solvents, forming a clear, colorless, and stable solution.
Upon hydrolysis, silanol groups are produced, which, through condensation reactions, form strong siloxane bonds (-Si-O-Si-). As more silanol groups form, hydrolysis and condensation occur simultaneously. The rates of hydrolysis and condensation are influenced by factors such as pH, concentration, solvent, temperature, and the presence of catalysts.












